Blackening Chemicals Guide
- Blackening, also known as black oxide coating or blackening treatment, is a process used to coat metals with a dark, corrosion-resistant layer. This finish is commonly applied to ferrous metals (like steel and
iron) but can also be applied to copper, brass, and zinc. The process is popular in the manufacturing, automotive, and firearms industries due to its ability to enhance appearance, reduce light reflection, and
improve corrosion resistance.
- Here’s a guide to the blackening process, including the types of chemicals used and the procedures involved:
- Types of Blackening Processes
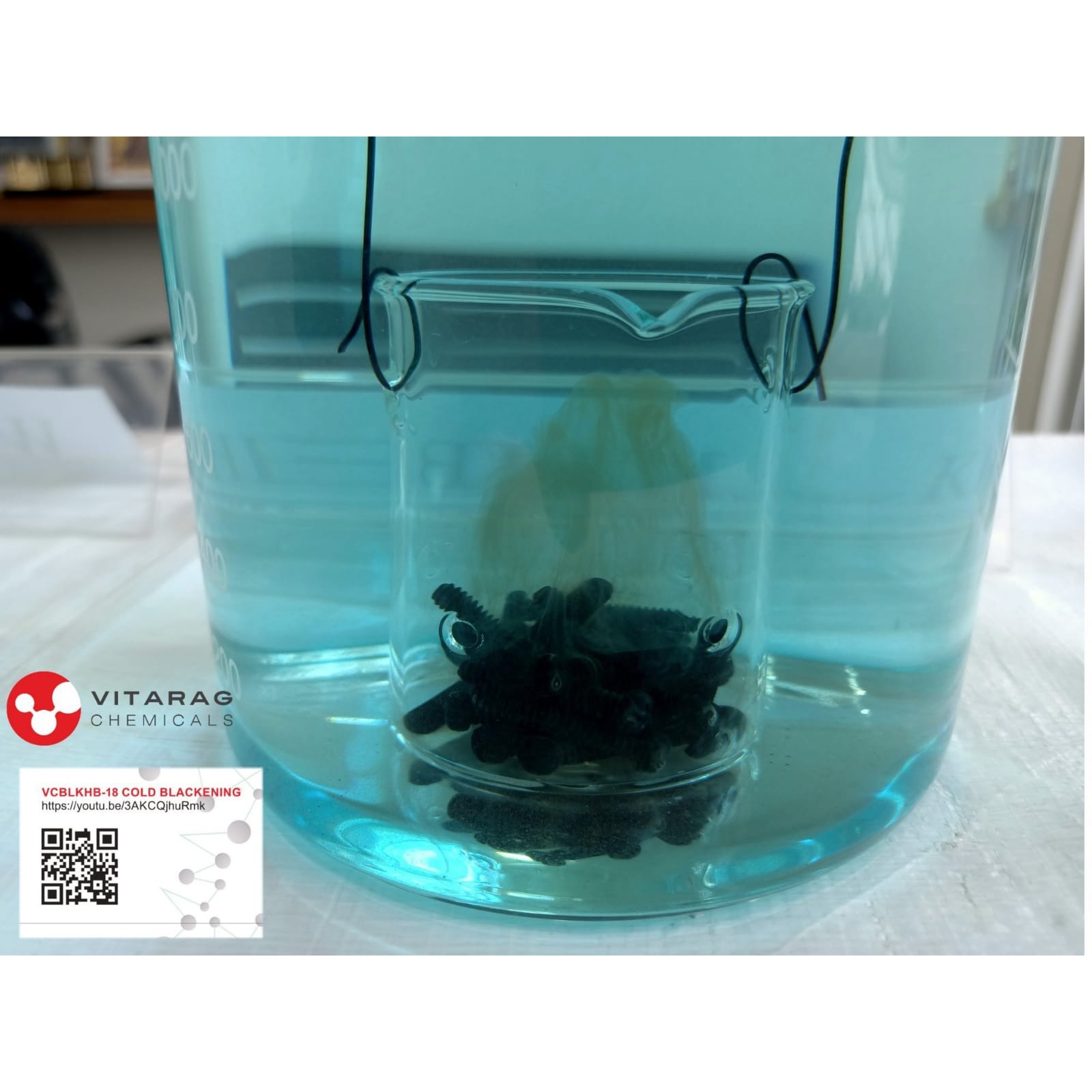
1. Cold Black Oxide:
- Suitable for steel, iron, copper, and brass.
- Involves room temperature chemical baths.
- The finish is not as durable as hot black oxide but is simpler and safer to apply.
- Common chemicals used: copper selenium compounds, which form a black copper selenide layer.
Keywords
ferrous metals
hot black oxide
Common chemicals
light reflection
Cold Black Oxide
firearms industries
black oxide coating
Blackening Processes
corrosion resistance
blackening treatment
copper selenium compounds
Blackening Chemicals Guide
black copper selenide layer
dark, corrosion-resistant layer
room temperature chemical baths