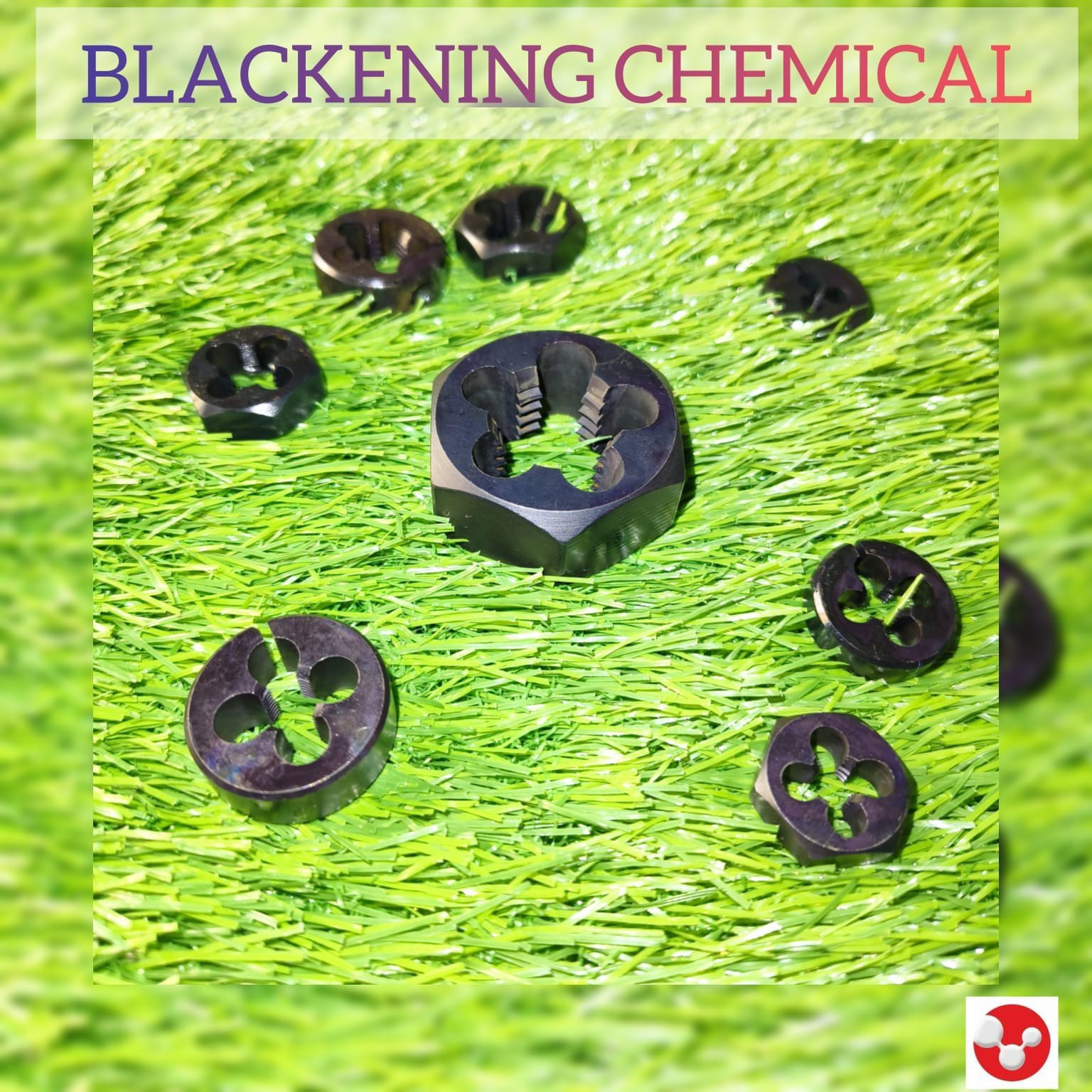
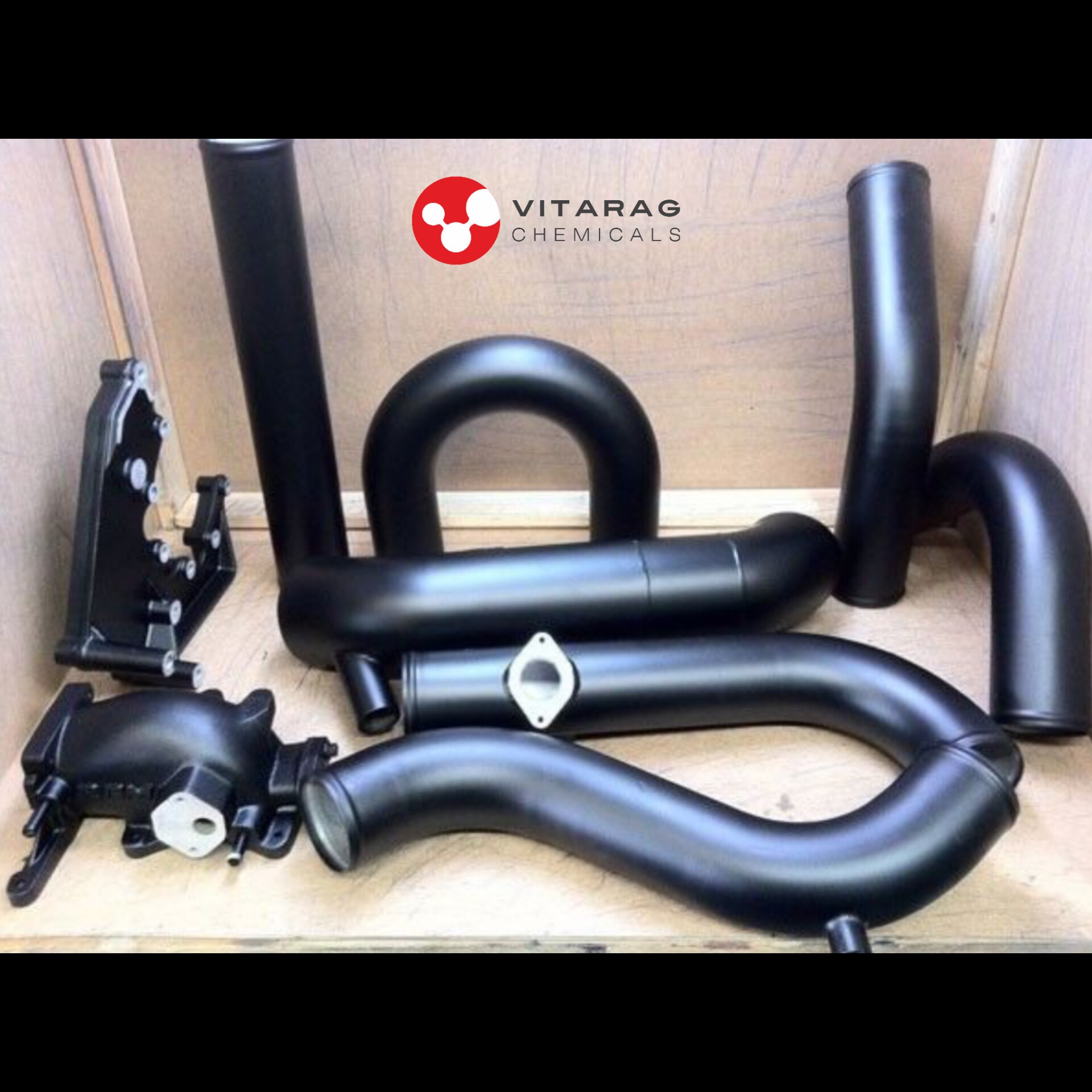
Metal Blackening Process
- Metal blackening, also known as black oxide coating, is a chemical process used to create a corrosion-resistant, decorative, and low-reflective black finish on ferrous and non-ferrous metals. This process is commonly used in automotive, firearms, tools, and industrial machinery to enhance aesthetics and durability.
* Types of Metal Blackening Processes
1. Hot Black Oxide (Hot Blackening)
- Performed at 140-150°C using an alkaline sodium hydroxide and nitrate/nitrite solution.
- Produces a deep black, corrosion-resistant finish.
- Requires post-treatment with oil or wax to enhance protection.
- Used for steel, stainless steel, and iron.
2. Cold Blackening (Cold Black Oxide)
- A room-temperature chemical conversion coating.
- Easier to apply but provides lower corrosion resistance compared to hot black oxide.
- Typically followed by an oil or sealant for better protection.
- Used for mild steel and iron in low-wear applications. # Blackening Chemical Manufacturer.
Keywords
enhance protection
chemical process
durability types
enhance aesthetics
industrial machinery
nonferrous metals
corrosionresistant decorative
mild steel
steel stainless steel
nitratenitrite solution produces
alkaline sodium hydroxide
automotive firearms tools
lowreflective black finish
black oxide coating