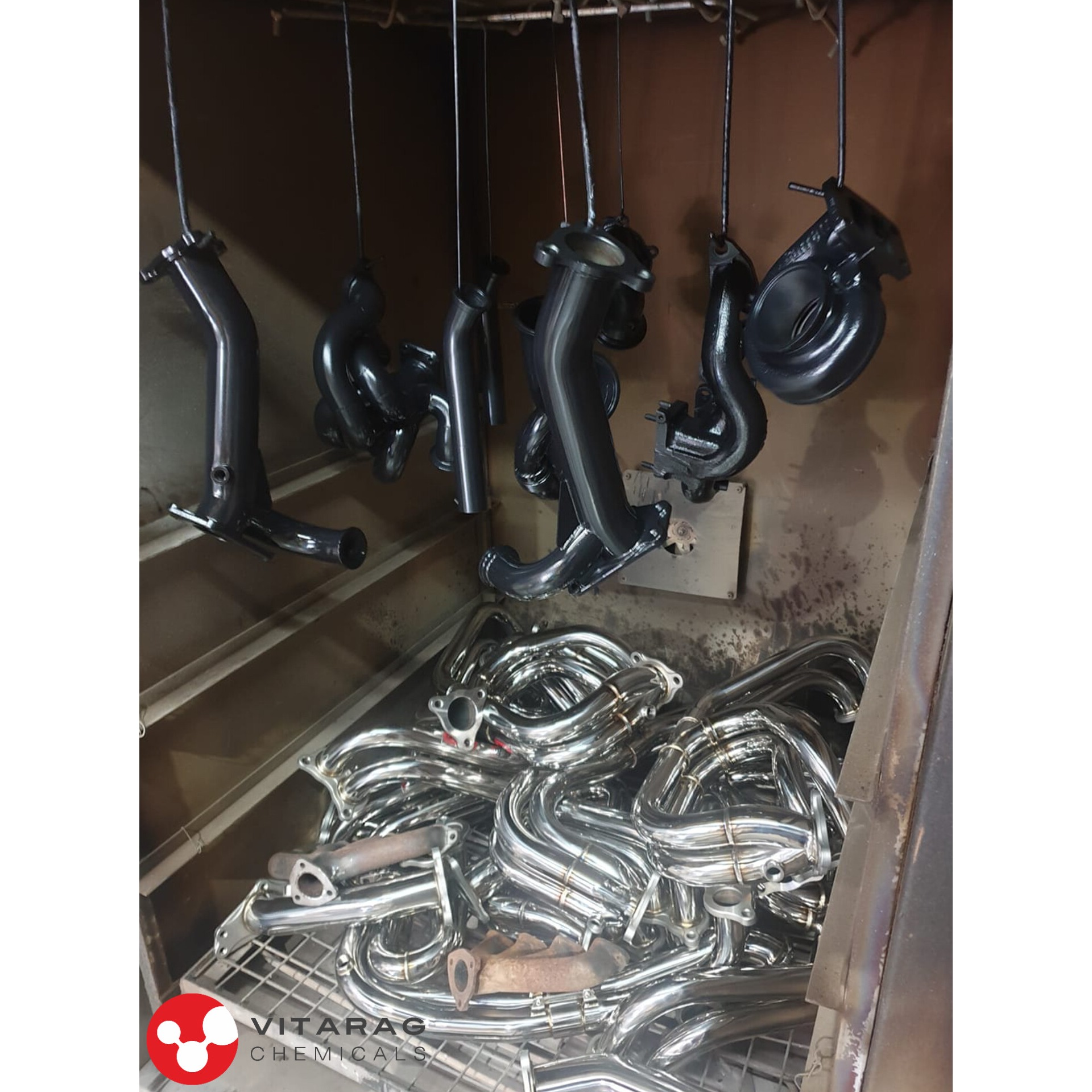
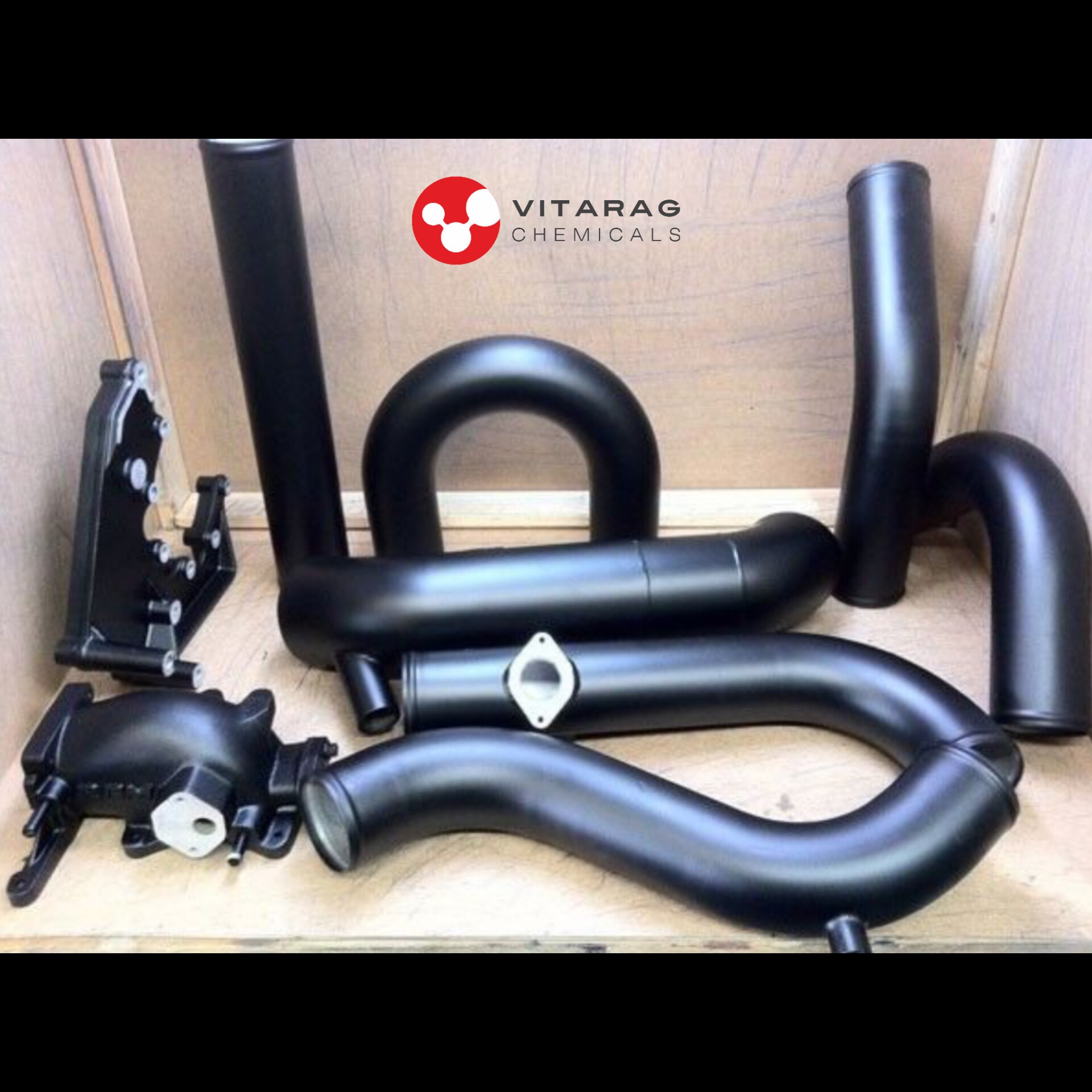
Blackening Agents For Metal
- Blackening agents for metal are chemical treatments used to create a black oxide or similar dark coating on metal surfaces, primarily for aesthetic purposes, corrosion resistance, and enhanced wear resistance. The process is also known as "black oxide coating, " "bluing, " or "patination, " depending on the specific metal and treatment method. Here are some common blackening methods and agents used for various metals:
1. Black Oxide Coating (Hot Blackening)
- Usage: Commonly applied to steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
- Process: The metal is submerged in an alkaline salt bath (usually sodium hydroxide) at high temperatures (around 140–150°C). This causes the surface of the metal to oxidize, forming a black iron oxide (magnetite, Fe₃O₄) layer.
- Advantages: Provides moderate corrosion protection, improves appearance, and maintains the dimensional integrity of the metal.
- Example Chemicals: Sodium hydroxide, sodium nitrate, or sodium nitrite.
Keywords
cast iron
Fe₃O₄) layer
specific metal
metal surfaces
sodium nitrite
sodium nitrate
various metals
Hot Blackening
stainless steel
wear resistance
sodium hydroxide
treatment method
black iron oxide
Blackening Agents
Example Chemicals
high temperatures
aesthetic purposes
alkaline salt bath
chemical treatments
black oxide coating
corrosion resistance
similar dark coating
dimensional integrity
common blackening methods
moderate corrosion protection